Leave Your Message
Choosing the right CPU heat sink is a critical component in optimizing your computer's performance and longevity. As processors become more powerful, the heat they generate increases, making efficient cooling solutions essential for maintaining operational stability. A well-designed CPU heat sink not only keeps temperatures in check but also ensures that your system runs smoothly under load, preventing throttling and hardware damage.
When selecting the best CPU heat sink, it is important to consider various factors such as compatibility with your CPU socket, thermal performance, and noise levels. With a myriad of options available on the market, understanding the fundamental principles of heat dissipation and airflow can greatly enhance your decision-making process. This guide will provide you with insights and criteria to help you navigate through the complexities of CPU heat sink choices, ensuring that you make an informed decision for your build or upgrade. Emphasizing efficiency and effectiveness, this exploration will serve as a comprehensive resource for achieving optimal performance in your computing endeavors.

When selecting a CPU heat sink, understanding the different types and their impact on performance is essential. There are primarily two categories of heat sinks: air coolers and liquid coolers. Air coolers are typically more straightforward and consist of a metal heatsink with one or more fans attached. They work by dissipating heat into the air, making them effective for most standard builds. On the other hand, liquid coolers utilize a liquid coolant to transfer heat away from the CPU to a radiator, where it is then dissipated. This method can be more efficient, especially in high-performance scenarios, as it often allows for better heat management, leading to lower temperatures during intensive tasks.
The choice between air and liquid coolers significantly affects thermal performance. Air coolers, while generally less expensive and easier to install, may struggle with heat dissipation in overclocked or highly demanding systems. Conversely, liquid coolers tend to provide superior cooling capacity and are ideal for overclocking enthusiasts seeking to maximize their CPU performance. However, they require more maintenance and can be more complex to install. Ultimately, understanding the nuances of each type allows users to choose a heat sink that aligns with their performance requirements and system configuration, ensuring optimal operation of their hardware.
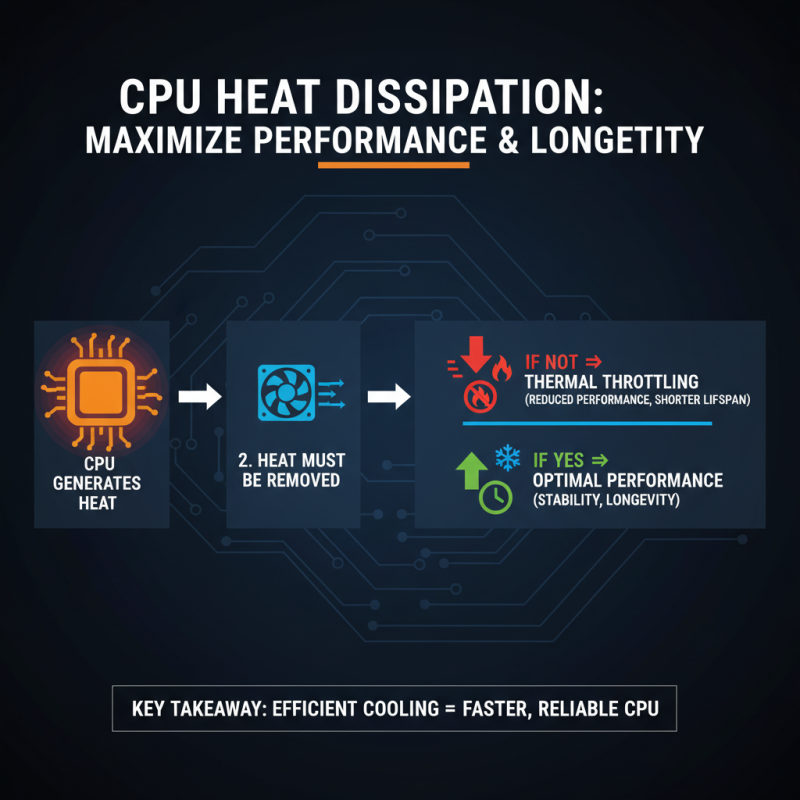
Heat dissipation plays a critical role in the performance and longevity of CPUs. When a processor is in operation, it generates heat, and if this heat is not effectively removed, it can lead to thermal throttling. This means that the CPU will reduce its performance to prevent overheating, ultimately affecting the system's overall efficiency. High temperatures can also shorten the lifespan of components, leading to potential hardware failures. Therefore, understanding the dynamics of thermal management is essential for anyone looking to maximize CPU performance.
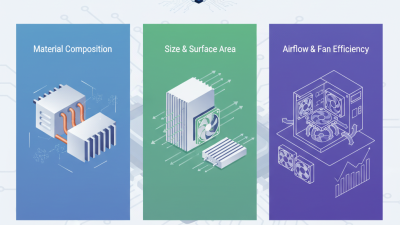
Choosing the right heat sink is vital because of the different designs and materials available that can enhance or hinder heat dissipation. Factors such as thermal conductivity, surface area, and airflow play crucial roles in how efficiently a heat sink can transfer heat away from the CPU. A well-designed heat sink will allow for optimal thermal performance, ensuring that the processor can operate at its full potential without the risk of overheating. As technology advances, the need for effective cooling solutions becomes even more paramount, making informed decisions on heat sink selection essential for achieving efficient CPU operation.

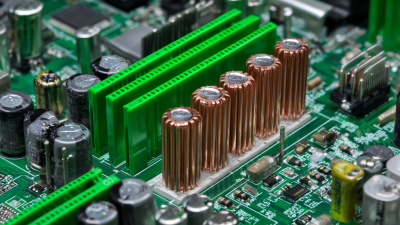
When selecting a CPU heat sink, one of the most critical considerations is the material used in its construction. The two primary contenders in heat sink design are aluminum and copper, each offering distinct advantages that can impact thermal performance. Aluminum is widely preferred due to its lightweight, cost-effectiveness, and good thermal conductivity. It is also easier to manufacture into complex shapes, allowing for versatile designs that can enhance airflow and cooling efficiency. These benefits make aluminum heat sinks popular among general users and budget-conscious builders.
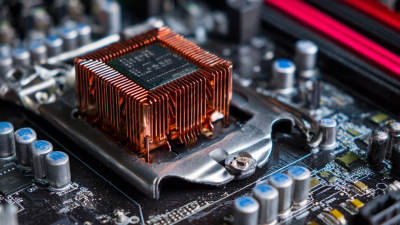
On the other hand, copper stands out for its superior thermal conductivity, which allows it to dissipate heat more effectively than aluminum. This makes copper heat sinks an excellent choice for high-performance applications where maintaining lower temperatures is crucial. However, copper's drawbacks include a heavier weight and a higher cost, which may deter some users. Additionally, copper can be more challenging to work with during fabrication, potentially limiting design options. Balancing performance needs with budget constraints is essential when determining the most suitable material for a CPU heat sink, as both aluminum and copper have unique characteristics that cater to different user preferences and requirements.
When selecting a CPU heat sink, understanding key metrics such as Thermal Design Power (TDP) and cooling capacity is essential for ensuring optimal performance. TDP represents the maximum amount of heat generated by a CPU under full load, which the cooling system must dissipate to maintain stability and efficiency. It’s crucial to choose a heat sink rated to handle at least the TDP of your CPU, as this ensures that there’s adequate cooling to prevent thermal throttling and maintain peak performance during intensive tasks.
In addition to TDP, evaluating the cooling capacity of a heat sink is vital. This metric indicates how effectively a cooling solution can transfer heat away from the CPU. Factors influencing cooling capacity include the surface area of the heat sink, the efficiency of the fan, and the quality of thermal interface materials. For optimal performance, look for configurations that combine larger surface areas with efficient airflow designs, allowing for more effective heat distribution. An understanding of these metrics will enable users to make informed decisions, ultimately leading to enhanced system performance and longevity.
When choosing a heat sink for your CPU, ensuring proper installation and compatibility is crucial for optimal thermal performance. An oversized heat sink may hinder RAM access or obstruct the motherboard layout, leading to installation difficulties. Conversely, a poorly fitted heat sink can result in inadequate heat dissipation, risking CPU overheating and diminished performance. Data from a recent industry report indicates that effective heat management can enhance CPU lifespan by up to 40%, highlighting the significance of choosing a compatible cooling solution.
One critical factor to consider is the socket type of your CPU. Various CPU models utilize different socket designs, and the heat sink must be tailored to fit securely onto it. A mismatch can lead to mounting issues, greatly impacting cooling efficiency. Additionally, the size and orientation of the heat sink are vital, as they need to fit within your case and align with motherboard components without obstructing airflow. Prior to installation, check the maximum heat sink dimensions specified in your CPU and motherboard manuals.
Tips: Before purchasing a heat sink, verify the thermal design power (TDP) of your CPU to select a model capable of handling its heat output effectively. Ensure the compatibility list provided by the manufacturer aligns with your CPU socket for a hassle-free installation. Using thermal paste correctly is also essential; applying too much or too little can affect heat transfer efficiency.