Leave Your Message
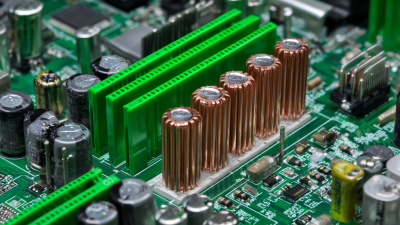
In the world of electronics design, efficient thermal management is crucial. One effective component is the Pcm Heat Sink. These heat sinks offer remarkable benefits, ensuring that electronic devices operate within safe temperature ranges. However, many designers overlook their potential.
Pcm Heat Sinks are designed to transfer heat away from critical electronics. The unique material properties enable excellent thermal conductivity. This feature helps extend the lifespan of components, reducing the risk of failure. But it's essential to consider placement and design. Poor integration can hinder performance, leading to unexpected heat build-up.
Effective thermal management is not just about choosing better materials. It requires thoughtful design and testing. The advantages of Pcm Heat Sinks go beyond mere efficiency. They enhance reliability, but installation must be precise. Designers need to pay attention to details to avoid common pitfalls.
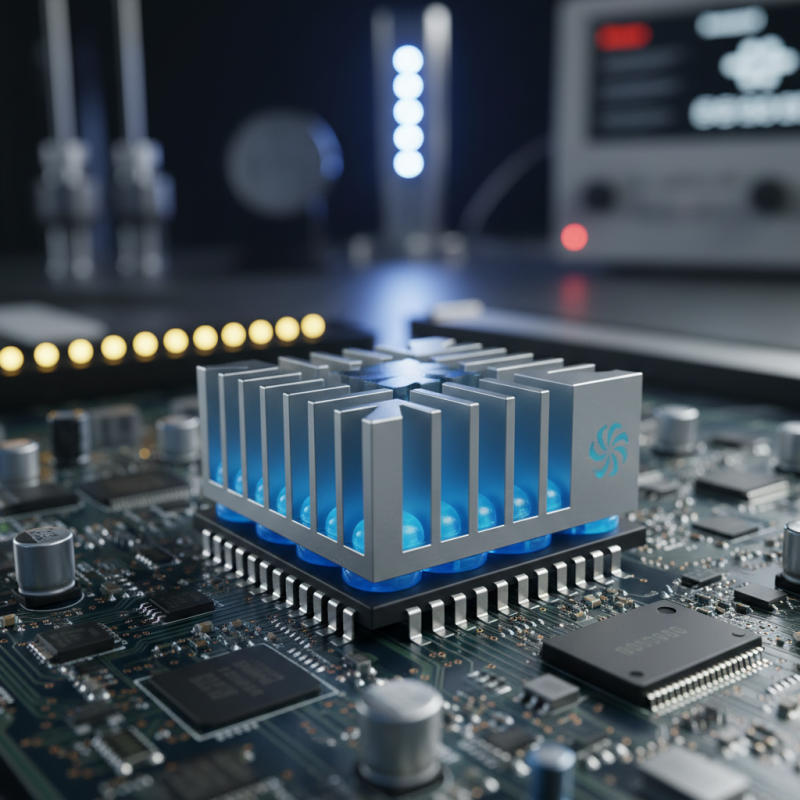
PCM heat sinks, or phase change material heat sinks, have emerged as a game changer in electronics design. These materials absorb and release heat as they change phases. This unique property allows for efficient thermal management, crucial for high-performance electronic devices. Research indicates that implementing PCM heat sinks can enhance heat dissipation efficiency by up to 50%. This could lead to longer device lifespans and improved reliability.
In electronics, overheating is a major concern. High temperatures can lead to component failure and reduced performance. Traditional cooling methods often fall short. PCM heat sinks provide a compact solution that can be integrated into various designs. Their ability to maintain a stable temperature can significantly enhance system performance. However, some designs may overlook the limitations of PCM materials. Not all environments are suitable for their use. Factors like cost and the weight of the heat sinks must also be considered.
While the data is promising, not every application may benefit equally. For example, the thermal conductivity of certain PCM materials can vary widely. This creates a need for careful selection and testing. Understanding the specific requirements of each design is essential. Ignoring these factors may lead to suboptimal performance, raising questions about reliability in critical applications.
Integrating Phase Change Material (PCM) heat sinks into electronics design presents notable advantages over traditional cooling systems. PCM heat sinks effectively absorb and release thermal energy, stabilizing temperature fluctuations. According to recent studies, these systems can improve thermal management by up to 30%, significantly increasing the efficiency of electronic components.
One of the main benefits is their lightweight nature. Traditional cooling systems can be bulky and require significant space. In contrast, PCM heat sinks occupy less volume, allowing for more compact designs. This is crucial for portable devices where space is limited. Additionally, PCM heat sinks operate silently, avoiding the noise generated by fans and other mechanical components.
Tips: When designing, consider the thermal load of your components. Precise calculations can enhance performance. Evaluate the phase change temperature of the PCM to match your specific needs.
However, there are challenges. PCM heat sinks may require more upfront investment and expertise in implementation. Moreover, the latent heat absorption can slow down initial cooling. Designers must weigh these factors carefully. Balancing performance and cost is essential for optimal results.
Phase Change Material (PCM) heat sinks are becoming essential in electronics design. Their ability to absorb, store, and release heat enhances device efficiency significantly. By maintaining optimal temperatures, these materials improve overall performance. Devices run cooler and longer, reducing thermal fatigue.
Implementing PCM heat sinks requires careful consideration. It's vital to choose the right PCM type based on the temperature range required. Sometimes, even small mistakes can lead to overheating. Testing is important, but it often gets overlooked.
Tips: Regularly monitor your device temperatures. Adjust the thermal management setup to ensure optimal performance. Understand that each design can have unique challenges. Not every solution will work perfectly the first time. Be open to tweaks and improvements. This will lead to more reliable and effective designs.
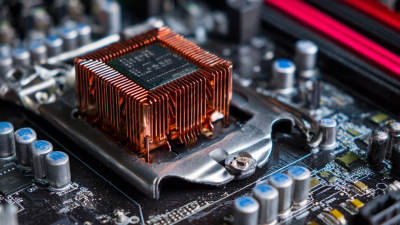
In electronics design, the integration of Phase Change Material (PCM) heat sinks requires careful consideration. PCM heat sinks can efficiently absorb and dissipate heat, enhancing device performance. According to a 2022 report from the International Journal of Thermal Sciences, proper thermal management can increase component lifespan by up to 30%. However, designers often overlook the placement and orientation of these heat sinks.
Material selection is crucial. Different PCMs have varying melting points and thermal properties. For instance, a PCM with a higher phase change temperature might suit high-power applications. Yet, it might not be ideal for devices with lower heat generation. Designers need to assess the specific thermal profiles of components they use. Overlooking these details can lead to overheating and device failure.
Additionally, the geometry of the heatsink plays a vital role. The effectiveness of a PCM heat sink is influenced by its surface area and volume. A compact design might fit better in tight spaces but could hinder heat transfer. A study by the Electronics Cooling magazine emphasizes that 40% of thermal issues arise from improper heat sink design. Designers must strive for a balance between size and efficiency, keeping functionality at the forefront.
The chart above illustrates the key benefits of utilizing PCM heat sinks in electronics design, emphasizing factors such as thermal conductivity, weight reduction, cost efficiency, form factor flexibility, and longevity. These features make PCM heat sinks a preferred choice for enhancing thermal management in various electronic applications.
The field of electronics is rapidly evolving. PCM heat sinks are gaining attention for their innovative capabilities. Future trends show an increasing shift towards enhanced thermal efficiency. Designers are focused on creating more compact models. This provides better performance without compromising space.
One exciting innovation in PCM technology is the integration of phase change materials. These materials can absorb and release heat effectively. They adapt to varying temperature conditions, ensuring optimal performance. However, incorporating such materials can complicate design processes. Balancing efficiency and cost remains a challenge for many engineers.
Additionally, advancements in manufacturing techniques are emerging. 3D printing, for instance, allows for customized designs. These designs can cater to specific thermal management needs. Still, the implications of such technologies raise questions. Will the long-term effectiveness match current methods? Exploring these advancements is essential as the industry moves forward.