Leave Your Message
In the race for superior thermal management, selecting the best Cooling Heat Sink is paramount. The demand for effective cooling solutions has surged, especially in high-performance electronics. According to a recent report by the Thermal Management Institute, over 70% of electronic failures are attributed to overheating. This highlights the critical role that a well-designed Cooling Heat Sink plays in ensuring device reliability and longevity.
Expert engineer Dr. Alex Chen emphasizes, “Choosing the right Cooling Heat Sink is not just about performance; it’s about future-proofing technology.” This statement underscores the necessity for engineers and designers to consider various options and innovations in heat sink technology. The market is evolving rapidly, with trends leaning towards materials like copper and advanced alloys that enhance thermal conductivity while reducing weight. However, many are still unaware of the true potential of these materials.
While the market offers numerous Cooling Heat Sink options, making an informed choice can be challenging. Factors such as size, airflow, and thermal interface material significantly impact effectiveness. Without addressing these aspects, even the most advanced designs can underperform. The quest for optimizing cooling solutions remains an ongoing journey in the electronics industry.

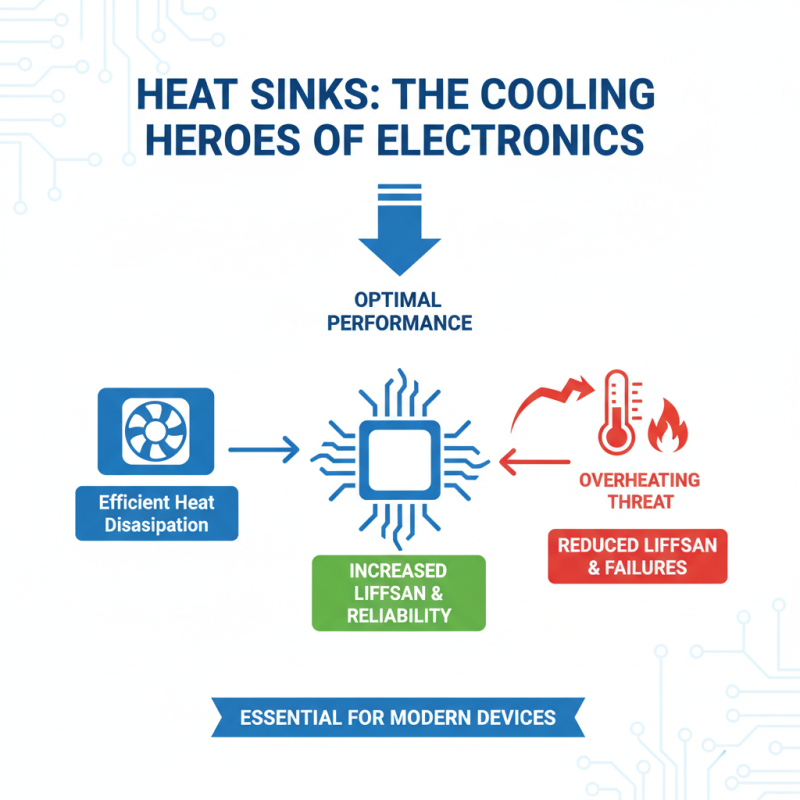
Heat sinks play a vital role in electronics. They help dissipate heat generated by electronic components. Efficient heat management is necessary for optimal device performance. Without effective cooling, devices can overheat. This may lead to reduced lifespan and reliability problems.
Understanding heat sink basics is crucial. These components come in various shapes and materials. Aluminum and copper are common choices. Large surface areas improve heat dissipation. However, size and design must also fit within device constraints. Not all heat sinks work equally well in every situation. The environment can affect cooling efficiency too.
Consider the mounting methods. Incorrect installation can reduce effectiveness. Thermal interface materials are also important. Selecting the right type can enhance heat transfer. In some cases, users struggle to find a balance between bulk and cooling power. Experimentation may be necessary to achieve optimal results. Ultimately, understanding heat sink fundamentals aids in making informed choices.
When it comes to heat sinks, understanding the types is crucial. Passive heat sinks rely on natural convection to dissipate heat. They are simple in design with no moving parts. This makes them reliable and often quieter. However, their performance can be limited in high-heat scenarios. The cooling capacity might not suffice for demanding applications.
Active heat sinks incorporate fans to enhance airflow. This approach increases cooling efficiency significantly. However, they introduce noise and complexity. Regular maintenance is essential to keep the fans running smoothly. Dust accumulation can hinder performance. In high temperatures, the active system may still struggle under heavy loads.
Hybrid solutions combine both passive and active elements. They aim to balance the benefits of both types. While they can be more effective, they may also prove more costly. Finding the right solution often involves trade-offs. It’s not just about effectiveness; considerations like size and power consumption matter as well. Embracing these factors can help optimize overall performance.
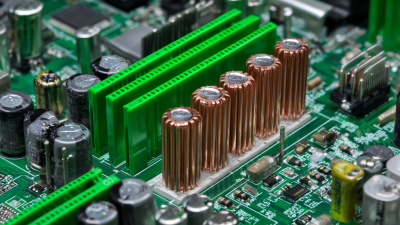
When it comes to heat sinks, materials play a crucial role in thermal management. Aluminum is a popular choice. It’s lightweight and cost-effective. Plus, it has good thermal conductivity. This makes it suitable for various applications. However, it might not always be enough for high-performance scenarios.
Copper, on the other hand, excels in conducting heat. Its density and thermal efficiency often outperform aluminum. Yet, copper is heavier and more expensive. Sometimes, the added cost may not justify the performance boost in lower-demand setups. It's essential to evaluate your specific needs carefully.
Innovative alternatives like graphite and thermal interface materials are also gaining traction. They offer unique benefits but may require more research. Balancing cost, weight, and performance is challenging. Every choice has trade-offs, and understanding them can help in making better decisions.
When selecting a heat sink, several factors play a crucial role in ensuring optimal cooling performance. The material is key. Aluminum and copper are popular choices. Aluminum is lightweight and cost-effective. Copper offers better thermal conductivity. The right choice depends on your specific cooling needs.
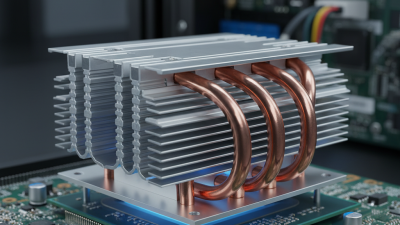
Another important factor is the design. Heat sink shapes can vary widely. Finned designs increase surface area, enhancing airflow. However, the size and weight need consideration. A larger heat sink might not fit in compact spaces. It’s a balancing act between performance and practicality.
Airflow is equally significant. Ensure your setup allows for sufficient ventilation. Passive cooling relies on natural air movement. In contrast, active cooling uses fans for enhanced airflow. Fans can help but introduce noise. Some users might find this irritating. It’s important to weigh noise levels against performance needs.
When selecting the best cooling heat sink models for 2026, it’s important to focus on key features. Look for heat sinks that offer excellent thermal conductivity. This ensures efficient heat dissipation. Models that combine lightweight materials with high performance are ideal for various applications. Consider the size and design as well. A compact model may meet your needs while maximizing airflow.
Tips: Always check compatibility. Not every heat sink fits all systems. Understand your cooling requirements. Do you need passive cooling or active? This can change your choice dramatically. Also, remember that aesthetics can matter. A visually appealing design may enhance your setup.
Many models have intricate fin designs. These can optimize airflow to enhance cooling performance. However, complexity might lead to cleaning challenges. Dust buildup can hinder efficiency. Choose designs that allow easy maintenance. Evaluate each model’s price-to-performance ratio. Sometimes, cheaper options fail to deliver. This could lead to overheating issues down the line. Reflect on your long-term needs versus immediate budget constraints.