Leave Your Message
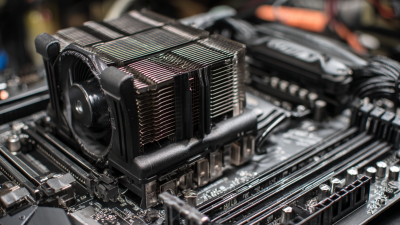
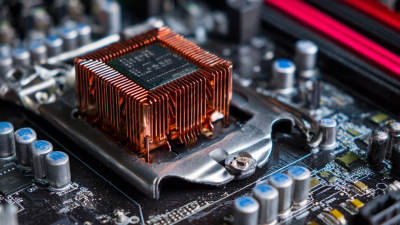
When it comes to maximizing the performance of your computer's CPU, the choice of heatsink is crucial. A well-chosen Copper CPU heatsink can make the difference between a smoothly running system and one that overheats and throttles under pressure. According to Dr. Emily Carter, a leading thermal management expert, "A high-quality copper CPU heatsink is essential for ensuring optimal heat dissipation and maintaining system stability." Her insights underscore the importance of understanding the myriad options available on the market today.
With the increasing capabilities of modern CPUs, the demand for effective cooling solutions has never been higher. Selecting the right Copper CPU heatsink requires careful consideration of factors such as thermal conductivity, design, and compatibility with your system. As you navigate this decision, it is valuable to have a clear understanding of the key characteristics that distinguish superior heatsinks from their lesser counterparts. In this guide, we will outline the top 10 tips for choosing the best Copper CPU heatsink tailored to your specific needs, ensuring that you get the most out of your computing performance.

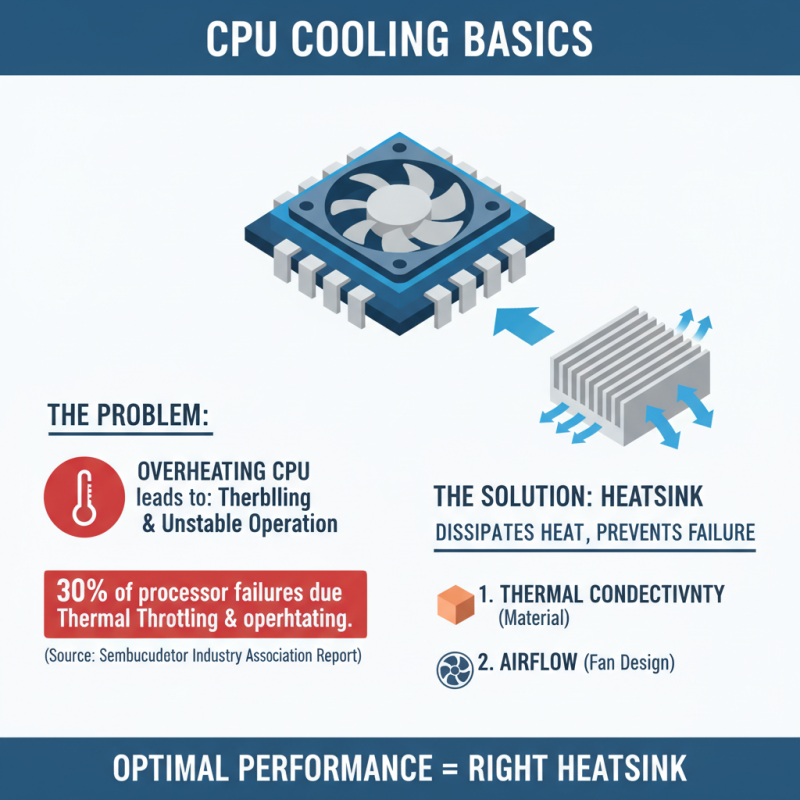
When it comes to maintaining optimal CPU performance, understanding the basics of heatsinks is crucial. A CPU heatsink serves the critical function of dissipating heat generated by the processor, preventing thermal throttling and ensuring stable operation. According to a report from the Semiconductor Industry Association, roughly 30% of processor failures are attributed to overheating. This statistic highlights the importance of selecting the right heatsink that effectively balances thermal conductivity and airflow.
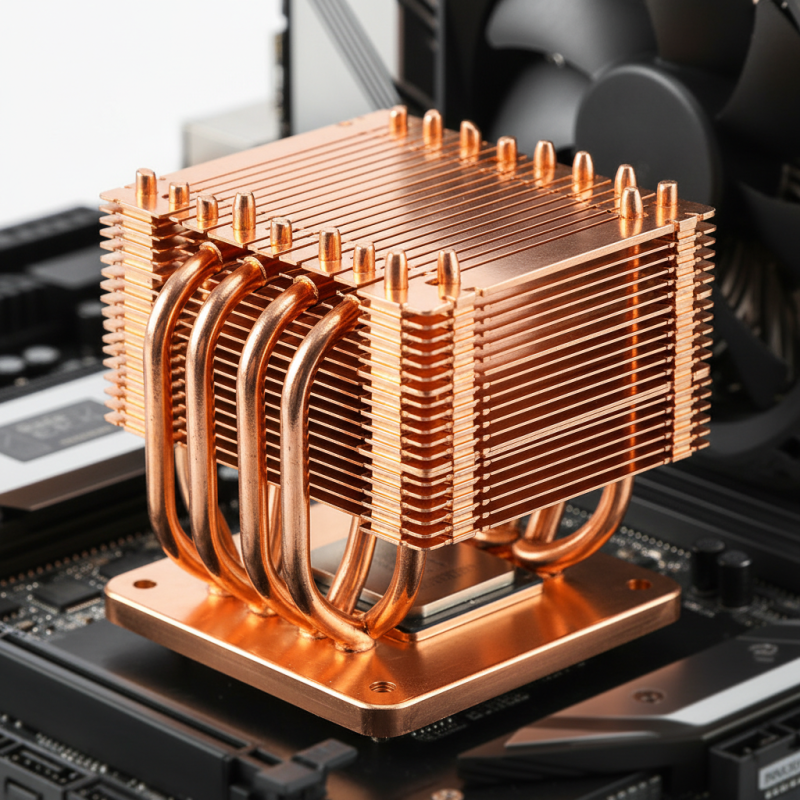
Copper heatsinks, known for their superior thermal conductivity, are particularly favored in high-performance applications. A study published in the Journal of Electronic Materials indicates that copper can dissipate heat up to 20% more efficiently than aluminum under comparable conditions. This makes copper an ideal choice for overclocking enthusiasts and users with demanding workloads. Additionally, the design of the heatsink, including fin spacing and fan compatibility, plays a significant role in thermal performance, making it essential for consumers to consider these factors when choosing a heatsink tailored to their specific needs.
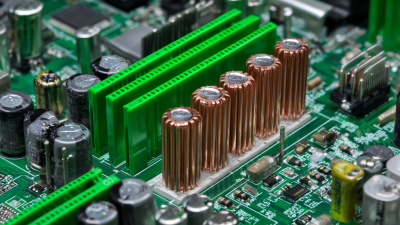
When evaluating the thermal conductivity of copper compared to other materials, it's essential to understand why copper is often considered the gold standard in heatsinks. Copper boasts a thermal conductivity of around 400 W/mK, significantly higher than aluminum, which averages about 200 W/mK. This superior conductivity means that copper can dissipate heat more efficiently, making it ideal for high-performance CPUs that generate substantial heat during operation. Therefore, if you're looking for a heatsink that can handle intense workloads and maintain optimal temperatures, copper is typically the way to go.
However, copper isn't the only option available. Some modern heatsinks incorporate mixed materials or advanced composites, aiming to balance weight, cost, and performance. For instance, certain aluminum heatsinks undergo anodization, enhancing their thermal performance and surface durability. Additionally, incorporating heat pipes filled with fluid in these heatsinks can improve temperature regulation by transferring heat away from the CPU more effectively. While copper remains a top contender, understanding these alternatives could provide solutions that meet specific needs or budgets without compromising much on performance.
| Material | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | Weight (grams) | Heat Dissipation Efficiency (%) | Cost ($) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | 401 | 500 | 90 | 25 |
| Aluminum | 205 | 600 | 80 | 15 |
| Copper/Aluminum Combo | 300 | 540 | 85 | 20 |
| Silver | 429 | 450 | 95 | 75 |
| Graphene | 2000 | 100 | 98 | 150 |
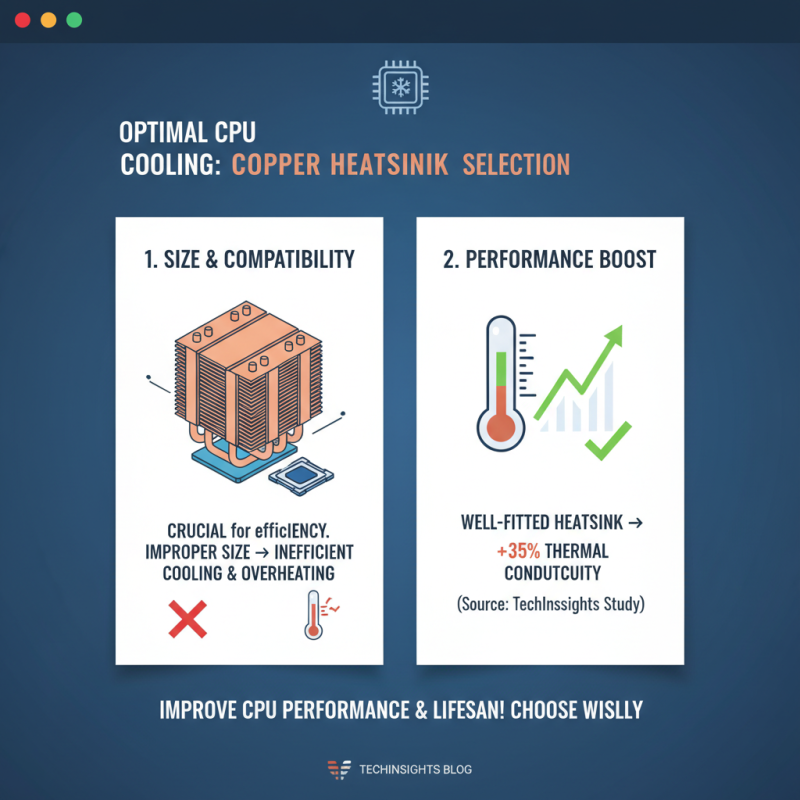
When selecting the right copper CPU heatsink, assessing size and compatibility is crucial. An improperly sized heatsink can lead to inefficient cooling and potential overheating, which could adversely affect your CPU's performance and lifespan. According to a recent study by TechInsights, a well-fitted heatsink can improve thermal conductivity by over 35%, ensuring optimal CPU temperatures under load.
To begin with, measure the area around your CPU socket, including the height restrictions imposed by nearby components such as RAM modules. A heatsink that is too tall may clash with your memory, leading to installation issues. Additionally, check your motherboard’s specifications to determine the compatible socket types. Many manufacturers provide specific dimensions and mounting options for their heatsinks, facilitating the selection process.
When choosing a heatsink, consider the TDP (Thermal Design Power) of your CPU. Copper is an excellent conductor of heat and is recommended for CPUs with a higher TDP, typically above 95W, as indicated in the Hardware Report 2023. Invest in a unit that meets or exceeds your CPU's thermal requirements to maintain performance under heavy workloads. This careful assessment will help ensure that you choose a heatsink that not only fits but also enhances your CPU's efficiency.
When selecting a copper CPU heatsink, one of the critical factors to consider is the type of fan used and its impact on cooling efficiency. The fan plays a pivotal role in heat dissipation, as it circulates airflow around the heatsink, enabling it to maintain optimal temperatures during operation. According to a study published by Tom's Hardware, the choice of fan can affect cooling performance by up to 25% depending on factors such as fan speed, design, and static pressure rating. High static pressure fans are particularly effective because they can push air more forcefully through the heatsink's fins, thus improving overall thermal performance.
Moreover, noise levels are also a significant consideration when selecting a fan for your copper heatsink. A report from AnandTech highlights that fans with larger diameters typically operate at lower RPMs while maintaining the same airflow, resulting in quieter performance. For example, 120mm fans can often provide better cooling efficiency while producing 10-15 dB less noise compared to their smaller counterparts. Therefore, when choosing a heatsink, paying close attention to fan options and their specifications can lead to improved cooling efficiency and a more enjoyable computing experience.
When selecting a copper CPU heatsink, one of the most significant factors to consider is the balance between cost and performance. High-performance heatsinks often come with a hefty price tag, which can be daunting for those on a tight budget. However, it's important to assess your specific needs: if you're running basic applications or do not overclock your CPU, a mid-range heatsink may suffice, allowing you to save money while still ensuring efficient cooling.
Conversely, for gamers or professionals engaging in resource-intensive tasks, investing in a premium copper heatsink can result in better thermal management and potentially longer CPU lifespan. Performance-oriented heatsinks often feature advanced designs, such as larger heat pipes and improved airflow capabilities, which justify their higher costs. Therefore, it's crucial to evaluate how much cooling performance you truly need and weigh that against your budget constraints to make an informed decision that best fits your computing requirements.