Leave Your Message
In the realm of thermal management, the significance of selecting the right Copper Heat Sink cannot be overstated. As technology continues to advance, engineers and designers face ever-increasing demands for efficient cooling solutions in various applications. Renowned thermal management expert Dr. Emily Carter emphasizes, "A well-chosen Copper Heat Sink not only enhances performance but also prolongs the lifespan of electronic components." This statement highlights the crucial role that effective thermal dissipation plays in maintaining system reliability.
Choosing the appropriate Copper Heat Sink can be a daunting task, with numerous factors to consider, including material properties, size, and design. As we delve into the essential tips for making an informed decision, it's important to recognize that the right heat sink can significantly influence the overall effectiveness of your project. With insights drawn from industry experts and practical considerations, this guide aims to equip you with the knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of Copper Heat Sink selection effectively.

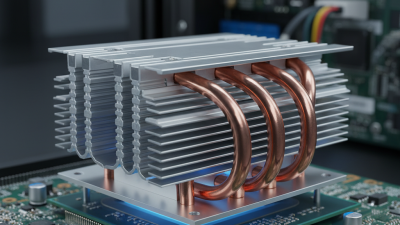
Copper heat sinks are essential components in thermal management, critical for dissipating heat generated by electronic devices. Their excellent thermal conductivity makes them ideal for applications where efficient heat transfer is paramount. Understanding the basics of copper heat sinks entails recognizing their structure and how they function. Typically made from solid copper or copper alloys, these heat sinks absorb heat from the source and distribute it into the surrounding air or through a cooling system, enhancing performance and prolonging device lifespan.
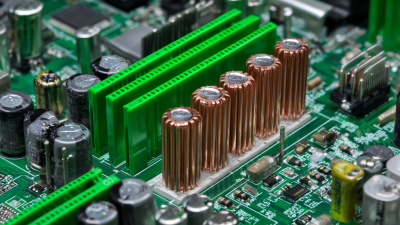
In practical applications, copper heat sinks are commonly found in computers, LED lighting, and power electronics, where heat must be effectively controlled to maintain optimal performance. The choice of a specific heat sink design, whether passive or active, depends on the project's requirements, including size constraints and cooling needs. Additionally, factors such as surface area, fin design, and mounting options play crucial roles in the effectiveness of a copper heat sink. By understanding these fundamentals, engineers can select the most suitable heat sink design that aligns with their project specifications and operational demands.
When selecting a copper heat sink for your project, evaluating heat transfer efficiency and thermal conductivity is crucial. Heat transfer efficiency is primarily determined by the ability of the heat sink to dissipate heat away from the source effectively. Copper, with its excellent thermal conductivity, allows for rapid heat transmission, making it an ideal choice for many applications. The design of the heat sink, including its surface area and fin structure, also plays a vital role in enhancing heat dissipation. Maximizing the surface area allows for greater exposure to the cooling medium, whether that's air or liquid, and can significantly improve overall efficiency.
Thermal conductivity, measured in watts per meter-kelvin (W/mK), describes how well a material conducts heat. Copper's thermal conductivity ranges around 400 W/mK, which is significantly higher than that of aluminum. This property is especially important in high-performance applications where heat must be managed to prevent component failure. When assessing copper heat sinks, consider not only the material’s conductivity but also how it interacts with its environment. Factors such as airflow, mounting conditions, and the surrounding materials can all affect the thermal performance of the heat sink. Careful consideration of these elements will help ensure that your project achieves optimal thermal management.
| Tip Number | Tip Description | Heat Transfer Efficiency | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Evaluate necessary heat dissipation based on component specifications. | High | 400 |
| 2 | Consider the ambient temperature where the heat sink will be used. | Medium | 385 |
| 3 | Select the proper size and form factor for the heat sink. | High | 393 |
| 4 | Evaluate the airflow around the heat sink. | High | 390 |
| 5 | Consider the surface area of the heat sink to maximize heat transfer. | Very High | 400 |
| 6 | Look for heat sinks with fins or additional structure to enhance cooling. | High | 402 |
| 7 | Determine if active cooling (fans) is needed in combination. | Very High | 385 |
| 8 | Check compatibility with the mounting setup of components. | Medium | 390 |
| 9 | Ensure the heat sink material is free of corrosion and oxidation. | High | 398 |
| 10 | Review and adhere to any industry standards applicable to your project. | Medium | 395 |

When selecting a copper heat sink, one of the most critical considerations is determining the appropriate size and shape to meet your project’s thermal management requirements. The dimensions of the heat sink directly influence its effectiveness in dissipating heat. A larger heat sink generally has more surface area, which can enhance heat dissipation. However, it must also fit within the spatial constraints of your project. Carefully measuring the available space ensures that you choose a heat sink that can be efficiently installed without compromising other components.
Furthermore, the shape of the heat sink plays a vital role in performance. Flat heat sinks may be ideal for compact designs, while finned or extruded shapes can maximize airflow and increase thermal performance. Considering factors such as the orientation of the heat sink, airflow direction, and proximity to other heat-generating components will help determine the best shape. Analyzing thermal simulations can also provide insight into how different configurations perform under load, ensuring that your choice effectively meets the cooling demands of your specific application.
When selecting a copper heat sink for your project, it's crucial to consider mounting options that ensure optimal thermal performance. The choice of mounting method can significantly impact heat transfer efficiency. Common mounting techniques include mechanical attachments, adhesive solutions, and press-fit systems. According to a recent industry analysis, effective mounting can enhance thermal conductivity by up to 15%, which is critical in high-performance applications. When assessing your project's requirements, ensure that the chosen mounting option provides a secure fit, minimizing any thermal interface resistance.
Another vital aspect is ensuring compatibility with your project's design and component layout. Some heat sinks come with pre-drilled holes or customizable bases to accommodate various configurations, which can be particularly beneficial in tight spaces. A report published by the Thermal Management Association indicated that improper compatibility can lead to a 20% decrease in thermal efficiency. Therefore, evaluate the dimensions and weight of the heat sink in relation to the surrounding components to achieve seamless integration.
Tip: Always measure the surface area that the heat sink will be placed on; good contact is essential for heat dissipation.
Moreover, consider the thermal requirements of your components when selecting the heat sink. An appropriately sized heat sink can significantly influence cooling performance. The right copper heat sink should match the thermal output of your components to effectively dissipate heat while maintaining safe operating temperatures.
Tip: Use simulation tools to predict thermal performance based on various heat sink designs before finalizing your choice.
When embarking on a project that requires effective thermal management, particularly one that leverages copper heat sinks, it is crucial to weigh the cost against performance. Copper is renowned for its superior heat conductivity, making it an excellent material choice. However, it can also be more expensive than alternatives like aluminum. Therefore, before making a decision, assess the specific thermal requirements of your project and determine whether the enhanced performance of copper justifies its higher price tag.
To make an informed decision, consider both the initial costs and long-term benefits. A high-performance copper heat sink may come with a higher upfront expense but can lead to better thermal efficiency, resulting in reduced energy consumption and longer component life span. For budget-conscious projects, it is essential to evaluate how much thermal management is essential for your application. In some cases, a less expensive aluminum heat sink might suffice, while others may necessitate the superior capabilities of copper. Balancing these factors is key to achieving optimal performance within your budget constraints.