Leave Your Message
A GPU heatsink is a crucial component in modern computing. It plays an essential role in managing the temperature of graphics processing units (GPUs). As gaming and graphic-intensive applications become more popular, effective cooling solutions are increasingly necessary. According to industry reports, overheating is one of the leading causes of GPU failure. A well-designed GPU heatsink can prolong the lifespan of these critical components.
The key function of a GPU heatsink is to dissipate heat generated during operations. Copper and aluminum are common materials used for heatsinks due to their excellent thermal conductivity. Many high-performance GPUs can produce heat exceeding 300 watts during peak usage. This emphasizes the need for efficient thermal management. However, not all heatsinks perform equally. Some designs may not adequately fit certain GPU models, leading to suboptimal cooling.
While the technology surrounding GPU heatsinks has advanced, challenges remain. Many users may choose aesthetics over functionality when selecting a heatsink. This decision could lead to overheating problems in the long run. Additionally, in a market where power consumption is rising, the demand for effective yet compact solutions is urgent. A GPU heatsink remains a critical topic in today’s tech landscape, urging continuous innovation and reflection.


A GPU heatsink is a critical component in a graphics processing unit's thermal management system. Its primary purpose is to dissipate heat generated during intense operations, such as gaming or 3D rendering. The average GPU can operate at temperatures ranging between 70 to 85 degrees Celsius. If not managed properly, performance can degrade, and components may fail. This underlines the importance of a well-designed heatsink.
Typically, a GPU heatsink is made of aluminum or copper. These materials have high thermal conductivity. They increase the surface area for heat dissipation through fins or heat pipes. For example, a high-end GPU can have a heatsink weighing over a kilogram. According to reports, effective cooling can improve a GPU's lifespan by up to 30%. This highlights the necessity of robust thermal solutions in modern graphics cards.
However, some designs fall short. Issues like airflow obstruction or inadequate thermal paste application can lead to overheating. A poorly installed heatsink may cause temperature spikes, defeating its purpose. Users need to be aware of these potential failures. As gaming trends push GPUs to their limits, attention to cooling solutions becomes even more crucial.
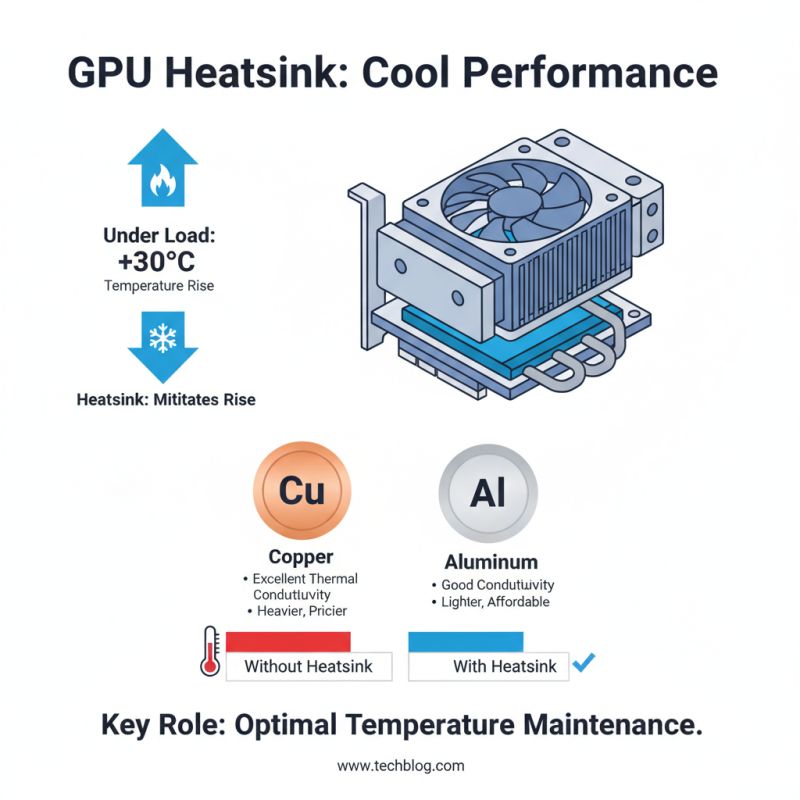
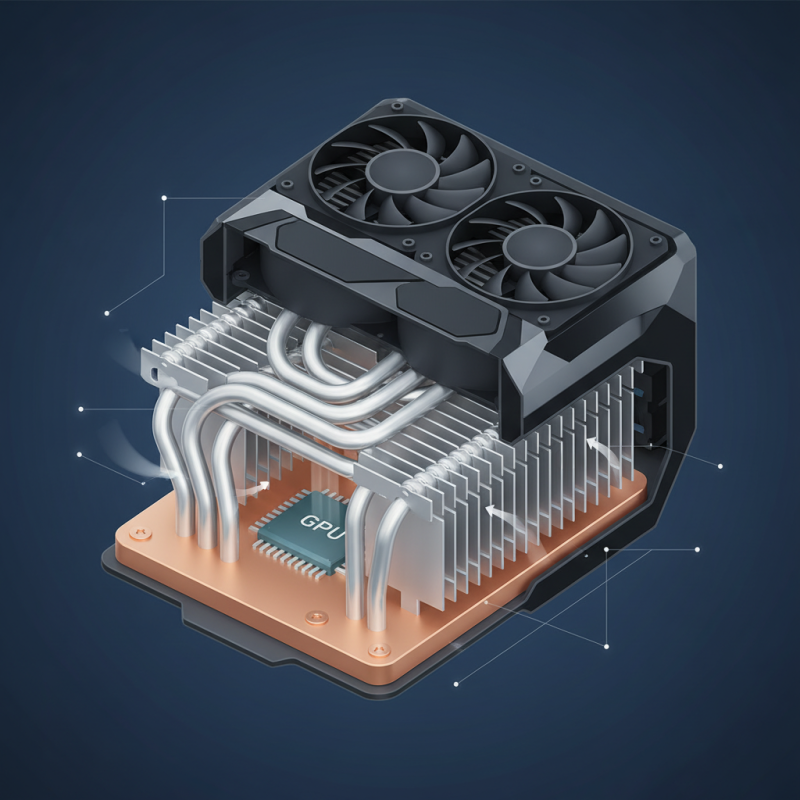
A GPU heatsink is essential for maintaining optimal temperatures during high-performance tasks. The structure typically comprises metal components, often aluminum or copper, due to their excellent thermal conductivity. Copper, although heavier and pricier, transfers heat more efficiently. Reports indicate that GPU temperatures can rise by 30°C or more under load. A well-designed heatsink can mitigate this rise.
Fins and heat pipes are crucial design elements. Fins increase surface area, allowing better airflow around the heatsink. Heat pipes, filled with liquid, facilitate rapid heat transfer away from critical components. Research shows that effective fins can enhance cooling performance by as much as 25%. However, design flaws can lead to hotspots, where temperature spikes occur despite the heatsink's presence.
Many models struggle with balancing size and performance. Larger heatsinks provide better cooling but may not fit all setups. It's clear that while materials and design play a significant role in efficiency, practical implementation often reveals shortcomings. A heatsink’s true potential can only be realized when addressing compatibility and airflow dynamics. These factors complicate the pursuit of an ideal cooling solution.
A GPU heatsink is a crucial component in managing heat generated during the intensive tasks of graphics processing. By adequately dissipating heat, it helps maintain optimal performance and prolongs the lifespan of the GPU. Understanding how they work unveils the principles of thermal conductivity, which is fundamental to efficient heat transfer.
Thermal conductivity relies on materials that conduct heat effectively. Metals like copper and aluminum are widely used. They have a high thermal conductivity, allowing heat to move quickly from the GPU to the heatsink's surface. As heat transfers, the heatsink's larger surface area dissipates heat into the surrounding air. This process often involves fans that further enhance airflow. However, the effectiveness of this design depends heavily on proper installation and airflow management.
Heat pipes are another interesting aspect of GPU heatsinks. They can transfer heat along specified paths, improving efficiency. Yet, not all configurations are ideal; sometimes, gaps can form between the GPU and the heatsink. This compromises heat transfer. Additionally, dust accumulation can obstruct airflow. Regular cleaning and maintenance become essential to ensure long-term performance.
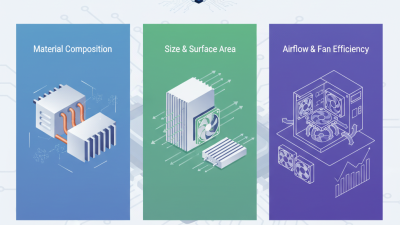
When assessing GPU heatsink efficiency, several performance metrics come into play. The crucial metrics include thermal impedance, airflow rate, and surface area. Thermal impedance measures how well the heatsink dissipates heat. A lower value indicates better performance, but achieving that can be challenging. Designs must balance size and weight with effectiveness.
Airflow rate is vital too. A heatsink can only cool if there’s adequate airflow over its fins. Many setups struggle with airflow. Poor case ventilation can undermine even the most advanced heatsinks. Surface area is another essential factor, as larger surface areas can dissipate more heat. Yet, this often leads to bulkier designs, which may not fit compact setups.
Despite advances in technology, real-world results can vary. Users may find that aftermarket improvements don’t significantly impact performance. Environmental factors, like ambient temperature, also play a vital role. Sometimes, it feels like a constant game of trial and error. Opting for a more efficient heatsink can prove difficult without proper testing. Understanding these metrics can lead to better choices in heatsink selections.
| Heatsink Type | Material | Surface Area (cm²) | Weight (g) | Cooling Efficiency (%) | Noise Level (dBA) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Passive Heatsink | Aluminum | 150 | 300 | 70 | N/A |
| Active Heatsink | Copper | 120 | 400 | 85 | 32 |
| Liquid Cooler | Aluminum & Copper | 200 | 500 | 90 | 25 |
| Hybrid Cooler | Aluminum with Water Cooling | 180 | 450 | 88 | 30 |
Future trends in GPU heatsink technology are marked by innovative cooling solutions. As GPUs become more powerful, efficient cooling methods are crucial. According to a recent report from Market Research Future, the global thermal management market for electronics is expected to reach $22 billion by 2025. This growth highlights the demand for advanced heatsink designs.
Emerging materials like graphene and advanced aluminum composites show promise in improving heat dissipation. These materials can significantly enhance thermal conductivity, with graphene being 200 times more conductive than copper. Innovative designs like heat pipes and vapor chambers are also gaining traction. These solutions offer better heat spread across the surface area, ensuring optimal GPU performance.
Despite the advancements, there are challenges. Not all designs achieve a perfect fit in varied GPU architectures. The balance between cooling efficiency and aesthetic design is often hard to strike. Additionally, thermal management solutions can be bulky, which may affect the overall size of PC builds. As technology advances, it will be essential to refine these cooling solutions to be both efficient and space-conscious.