Leave Your Message
In the rapidly evolving world of electronics, effective thermal management has become a critical factor in ensuring the performance and longevity of devices. As technology advances, components generate more heat, making the implementation of efficient thermal solutions paramount. According to Dr. Emily Foster, a leading expert in thermal management and the CEO of ThermoTech, “The choice of heat sink can significantly influence the reliability and efficiency of electronic systems.” This underscores the importance of selecting the right heat sink solution to maintain optimal operating temperatures.
In this article, we will explore the top 10 heat sink solutions that stand out in the industry for their efficacy in thermal management. With advancements in materials and design, modern heat sinks are more effective than ever in dissipating heat and preventing overheating. From passive to active cooling solutions, these options are vital for maintaining the performance of high-demand electronic devices. By examining these solutions, we aim to provide insights that will aid engineers and designers in their quest for optimal thermal performance, ensuring that their innovative designs can succeed in a thermally challenging environment.
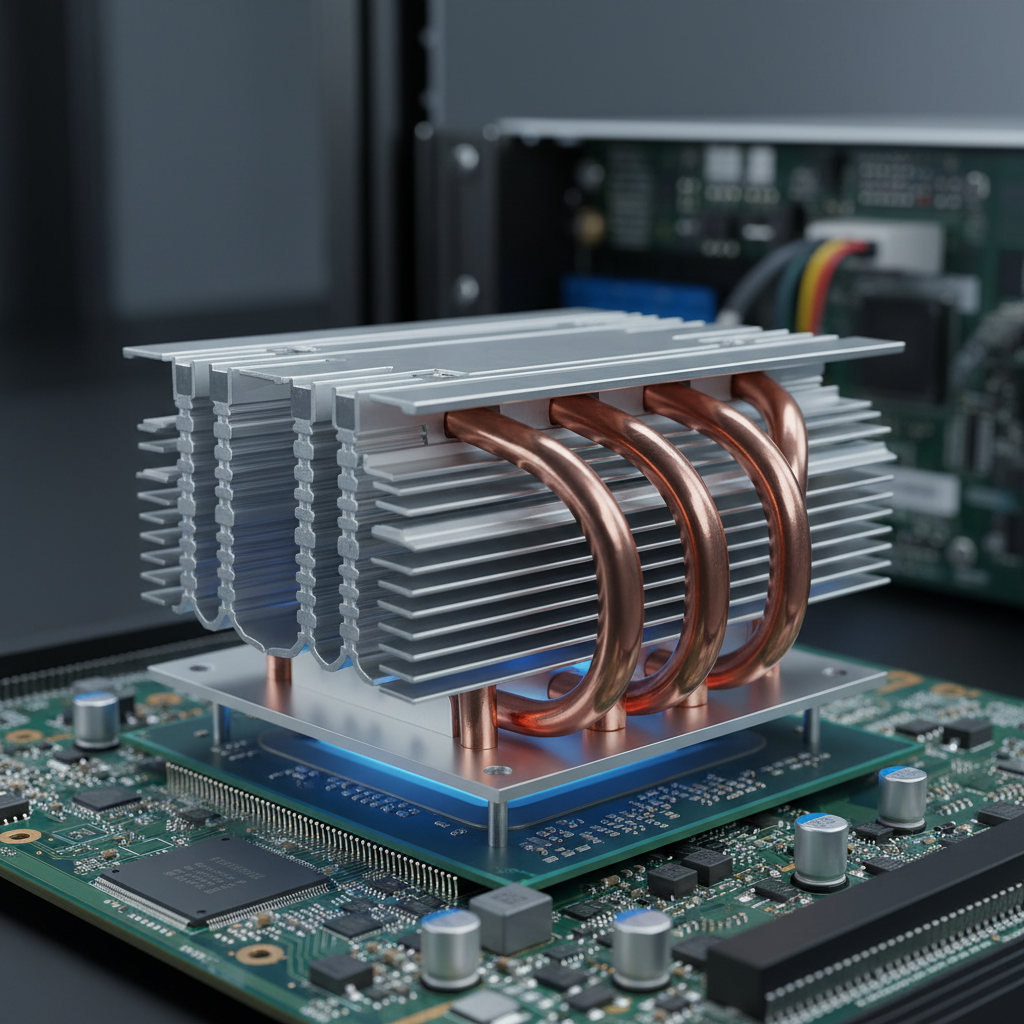

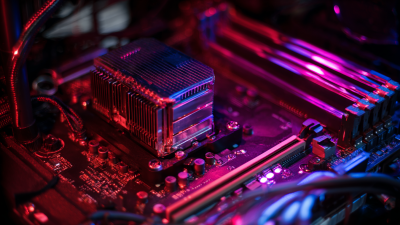
Heat sinks are crucial components in electronic devices, designed to dissipate heat generated by electronic components such as CPUs, GPUs, and power transistors. Understanding the basics of heat sinks is essential for achieving optimal thermal management in electronics. These devices function by increasing the surface area that is exposed to the air, allowing effective heat transfer through convection and conduction. Materials commonly used for heat sinks include aluminum and copper due to their excellent thermal conductivity, making them ideal for enhancing heat dissipation.
The importance of heat sinks in electronics cannot be overstated. Excessive heat can lead to reduced performance, shortened lifespan, and even failure of electronic components. By efficiently removing heat, heat sinks help maintain operational temperature ranges that ensure reliability and efficiency. Furthermore, proper thermal management can improve overall system performance, enabling devices to run faster and operate at lower power consumption levels. As electronics continue to evolve, understanding and implementing effective heat sink solutions will be vital for engineers and designers in maintaining the integrity and longevity of their products.
| Rank | Heat Sink Type | Material | Application | Efficiency (°C/W) | Dimensions (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Extruded Aluminum | Aluminum | General Electronics | 5.0 | 100x50x20 |
| 2 | Core Heat Sink | Copper | High-Power Devices | 3.2 | 80x80x25 |
| 3 | Active Cooling Heat Sink | Aluminum + Fan | Computing | 2.5 | 150x150x30 |
| 4 | Heat Pipes | Copper | High-Performance CPUs | 2.0 | 50x50x5 |
| 5 | Finned Heat Sink | Aluminum | Power Amplifiers | 4.0 | 120x75x30 |
| 6 | Thermal Interface Material | Compound | All Applications | 1.5 | N/A |
| 7 | Embedded Heat Sink | Aluminum | Mobile Devices | 3.5 | 60x30x15 |
| 8 | Liquid Cooling System | Various | Gaming PCs | 1.0 | N/A |
| 9 | Soldered Heat Sink | Copper | Industrial Electronics | 3.8 | 40x40x10 |
| 10 | Custom Heat Sink | Aluminum/Copper | Specialized Applications | Varies | Varies |

In the realm of electronics, effective thermal management is crucial to ensure optimal performance and longevity of components. Innovative heat sink materials are at the forefront of this evolution, pushing the boundaries of traditional thermal management solutions. For instance, the introduction of graphene and carbon nanotubes has significantly enhanced thermal conductivity compared to conventional metals like aluminum and copper. These advanced materials not only provide superior heat dissipation but also contribute to lightweight designs, which are essential for miniaturized electronic devices.
Moreover, phase change materials (PCMs) are gaining traction in thermal management applications. By absorbing and releasing heat as they transition between solid and liquid states, PCMs can regulate temperatures more effectively than static heat sinks. Incorporating these materials into heat sink designs leads to improved thermal stability, with the potential to increase the reliability of electronic systems in high-performance settings. As the demand for high-efficiency electronics continues to rise, the exploration of novel materials and designs will be pivotal in revolutionizing thermal management strategies in the industry.
The demand for advanced thermal management solutions in electronics has spurred innovative approaches, particularly in active cooling techniques. One noteworthy method is the development of next-generation Peltier cooling systems. Pioneered through high-efficiency thin-film semiconductor technology, these refrigerant-free devices utilize nano-engineering to achieve superior performance. Such advancements promise to enhance heat dissipation in electronic components, crucial for maintaining optimal operational conditions without relying on traditional refrigerants.
Another revolutionary approach is the application of magneto-hydrodynamic behavior in magnetic nanofluids within mini-channel heat sinks. This cutting-edge technique addresses the increasing thermal challenges posed by high-density electronic devices and data centers. By leveraging the unique properties of magnetic nanofluids, engineers can create more efficient cooling solutions that not only meet the growing demands of the electronics market but also contribute to sustainable thermal management practices. As the industry continues to evolve, the integration of intelligent air-cooling solutions further complements these advancements, offering targeted cooling capabilities and maximizing the thermal efficiency of modern devices.
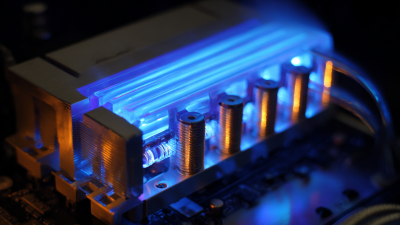
When it comes to thermal management in electronics, the choice between passive and active heat sink solutions is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and reliability. Passive heat sinks, typically composed of materials with high thermal conductivity like aluminum or copper, rely on natural convection to dissipate heat. They are often simpler in design, require no additional power, and are generally quieter, making them ideal for smaller electronics where space and noise are considerations. However, their efficiency can be limited, especially in high-power applications where heat generation exceeds passive dissipation capabilities.
On the other hand, active heat sinks incorporate fans or pumps to enhance airflow or fluid movement, significantly improving cooling performance. This method is particularly effective in scenarios where components generate substantial heat that must be rapidly managed to maintain operational stability. While active solutions are more complex and can introduce additional noise and power consumption, their efficiency in high-demand electronics environments is unmatched. Evaluating these two approaches involves considering factors such as application requirements, thermal loads, and environmental conditions, ultimately guiding the selection of the most suitable thermal management strategy for specific electronic devices.
Future trends in heat sink technology are poised to significantly influence electronic design, especially with the growing demands for compact and energy-efficient systems. The integration of nanomaterials into heat sink production is one of the most promising developments, enhancing thermal conductivity by up to 50% compared to traditional materials like aluminum and copper. According to a recent market analysis by Research and Markets, the global market for advanced heat sink solutions is expected to reach $2.5 billion by 2025, driven by innovations in thermal management.
Another key trend is the increasing adoption of 3D printing in the fabrication of heat sinks. This method allows for complex geometries that optimize airflow and enhance cooling performance, tailored to specific electronic applications. A study from TechInsights reveals that manufacturers utilizing additive manufacturing techniques report a 30% reduction in production costs and time, while also enabling the design of lightweight structures that preserve the necessary thermal efficiencies.
As these technologies evolve, they will redefine the capabilities of thermal management systems, paving the way for the next generation of high-performance electronics.